How to create 3D Animated Video Using Auto desk Maya Software with Texturing-Lightening-Visual Effects
How to create 3D Animated Video Using Auto desk Maya Software with Texturing-Lightening-Visual Effects.
Contents
- 0.1 How to Create a 3D Animated Video Using Autodesk Maya
- 0.2 Step 1: Pre-Production (Planning)
- 0.3 Step 2: 3D Modeling
- 0.4 Step 3: Texturing & UV Mapping
- 0.5 Step 4: Rigging & Skinning
- 0.6 Step 5: Animation
- 0.7 Step 6: Lighting & Rendering
- 0.8 Step 7: Visual Effects (VFX) & Simulation
- 0.9 Step 8: Rendering & Exporting
- 0.10 Step 9: Post-Production & Editing
- 0.11 Recommended Software Along with Maya
- 1 🎬 Step-by-Step Process to Create a 3D Animated Video in Maya
- 2 🛠️ Software/Tools You Can Use Alongside Maya
- 3 ✅ Tips for Beginners
How to Create a 3D Animated Video Using Autodesk Maya
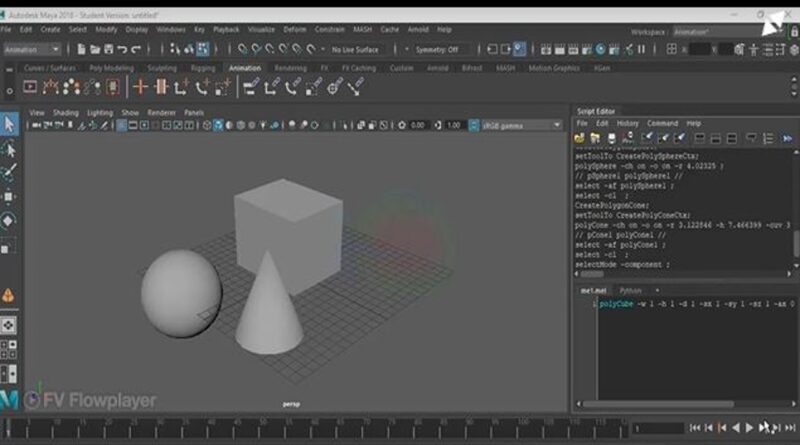
Autodesk Maya is a powerful software used for 3D modeling, animation, texturing, lighting, and visual effects (VFX). Here’s a step-by-step guide to creating a 3D animated video in Maya:
Step 1: Pre-Production (Planning)
Concept & Storyboarding – Sketch out the scenes and sequences.
Scriptwriting – Define dialogues, actions, and camera movements.
Character & Environment Design – Plan models, textures, and lighting.
Step 2: 3D Modeling
Create 3D Objects – Use polygons, NURBS, and curves to design characters, props, and environments.
Refine Meshes – Add details using sculpting tools.
Topology Optimization – Ensure smooth animation with proper edge loops.
Step 3: Texturing & UV Mapping
Apply Materials & Textures
Unwrap UVs for detailed painting (UV Editor).
Use tools like Substance Painter or Photoshop to create realistic textures.
Apply shaders in Arnold Renderer, Lambert, Phong, or Blinn for different material effects.
Step 4: Rigging & Skinning
Add Bones & Controllers
Use Maya’s Human IK (HIK) for auto-rigging characters.
Apply Inverse Kinematics (IK) & Forward Kinematics (FK) for smooth movements.
Bind skin using Smooth Bind or Rigid Bind.
Step 5: Animation
Keyframing & Motion Control
Use Keyframe Animation (Set Position, Rotation, and Scale over time).
Apply Graph Editor to refine motion curves.
Use Blend Shapes for facial animations.
Utilize Motion Capture (Mocap) Data for realistic movements.
Step 6: Lighting & Rendering
Create Realistic Lighting
Add Area Lights, Spotlights, and Directional Lights for depth.
Use Arnold Renderer for realistic shadows and reflections.
Adjust Global Illumination (GI) & Ambient Occlusion (AO) for better quality.
Step 7: Visual Effects (VFX) & Simulation
Enhance with Effects
Use Maya Bifrost for fluid, smoke, and fire simulations.
Apply nCloth for realistic fabric movement.
Add Particles & Dynamics for explosions, sparks, or magic effects.
Step 8: Rendering & Exporting
Finalizing the Animation
Use Batch Rendering in Arnold or RenderMan.
Export frames in EXR or PNG format for high quality.
Assemble scenes in After Effects or Premiere Pro for post-production.
Step 9: Post-Production & Editing
Add Music & Effects
Apply background music, voiceovers, and sound effects.
Color correct & enhance visuals in After Effects.
Export the final video in MP4, MOV, or AVI format.
Recommended Software Along with Maya
ZBrush – For high-detail sculpting.
Substance Painter – For realistic texturing.
Adobe After Effects – For post-production & compositing.
Blender/Nuke – For advanced VFX.
Would you like video tutorials, project files, or sample templates to get started?
Creating a 3D animated video using Autodesk Maya involves several stages of the 3D production pipeline, including modeling, texturing, lighting, animation, rendering, and visual effects (VFX). Below is a step-by-step guide, ideal for beginners to intermediate users.
🎬 Step-by-Step Process to Create a 3D Animated Video in Maya
🔹 1. Pre-Production
Before jumping into Maya:
-
✅ Create a storyboard
-
✅ Write a script
-
✅ Design character/environment concept art
-
✅ Plan camera angles and animation sequences
🧱 2. Modeling
Create 3D geometry (characters, props, environment)
-
Use polygon tools (
Mesh > Create,Extrude,Insert Edge Loop) -
Keep geometry clean and low-poly initially
-
Use NURBS for smooth, curved surfaces
-
Organize with layers and naming conventions
🎨 3. Texturing (UV Mapping)
Apply color, patterns, and details to your models
-
Open UV Editor:
UV > UV Editor -
Unwrap model using:
-
Planar / Automatic / Camera Projection
-
-
Export UV layout and paint in Photoshop or Substance Painter
-
Apply textures using Hypershade:
-
Connect Color, Bump, Specular maps
-
💡 4. Lighting
Create realistic or stylized lighting
-
Use Arnold Lights:
-
Area Light,Skydome Light,Spot Light
-
-
Adjust intensity, exposure, color temperature
-
Use three-point lighting for characters
-
Test lighting with Arnold RenderView
🎥 5. Camera Setup
Control what the viewer sees
-
Create a camera:
Create > Camera -
Use keyframes for camera movement (
Sto set key) -
Try cinematic shots: dolly, pan, zoom, etc.
🏃♂️ 6. Rigging & Skinning (for characters only)
Prepare your model for animation
-
Add joint chains (
Skeleton > Create Joints) -
Use Skin > Bind Skin
-
Create IK/FK handles
-
Add controls using NURBS circles for animators
🕺 7. Animation
Bring your characters and objects to life
-
Animate using Timeline and Graph Editor
-
Use keyframing (S) at important frames
-
Apply motion path for smooth movement
-
Use constraints and Set Driven Key for complex actions
🌫️ 8. Visual Effects (FX)
Add fire, smoke, cloth, particles, etc.
-
Use nParticles: rain, smoke, sparks
-
Use Bifrost for water and fluids
-
Use nCloth for cloth simulation
-
Use MASH for motion graphics
🖼️ 9. Rendering
Export your final video frames
-
Use Arnold Renderer for realism
-
Set output size:
Render Settings > Image Size -
Set file type: EXR, PNG, JPEG
-
Batch render your scene to images (
Render > Batch Render)
🎞️ 10. Post-Production
Combine, edit, and finalize
-
Import image sequence into After Effects, Premiere Pro, or DaVinci Resolve
-
Add:
-
Background music
-
Sound effects
-
Color grading
-
Final VFX overlays
-
🛠️ Software/Tools You Can Use Alongside Maya
| Purpose | Software |
|---|---|
| Texture Painting | Adobe Photoshop, Substance 3D |
| Compositing | After Effects, Nuke |
| Video Editing | Premiere Pro, DaVinci Resolve |
| Sound Design | Audacity, FL Studio |
✅ Tips for Beginners
-
Save frequently, use incremental saves
-
Use low-res playblasts to preview animation
-
Use references for realistic motion
-
Keep scene clean and organized
-
Learn basic Python/MEL scripting for automation
Would you like:
-
A sample Maya project file?
-
A video tutorial link playlist?
-
A checklist PDF of this entire pipeline?
Let me know your preferred format!