Wireless and Mobile Communication Introduction and Basic Concept
Wireless and Mobile Communication Introduction and Basic Concept
Contents
- 0.1 Wireless and Mobile Communication – Introduction & Basic Concepts
- 0.2 1. What is Wireless Communication?
- 0.3 Key Characteristics of Wireless Communication
- 0.4 2. What is Mobile Communication?
- 0.5 Key Features of Mobile Communication
- 0.6 3. Basic Components of Wireless & Mobile Communication
- 0.7 1. Transmitter – Converts information into signals (Example: Mobile phone, Wi-Fi router)
- 0.8 2. Receiver – Receives and decodes signals (Example: Another mobile phone, computer)
- 0.9 3. Medium (Channel) – Air or space where signals travel (Example: Radio waves, Infrared)
- 0.10 4. Antennas – Used to send and receive signals (Example: Mobile towers, satellite dishes)
- 0.11 5. Base Station (Cell Tower) – Connects mobile devices to the network
- 0.12 4. Types of Wireless Communication Technologies
- 0.13 A. Cellular Communication (Mobile Networks)
- 0.14 B. Wireless LAN (Wi-Fi)
- 0.15 C. Bluetooth
- 0.16 D. Satellite Communication
- 0.17 E. Infrared (IR) Communication
- 0.18 5. Advantages & Disadvantages of Wireless Communication
- 0.19 Advantages
- 0.20 Disadvantages
- 0.21 6. Applications of Wireless & Mobile Communication
- 0.22 Conclusion
- 0.23 Wireless and Mobile Communication Introduction and Basic Concept
- 0.24 UNIT 1 INTRODUCTION TO MOBILE COMMUNICATIONS
- 0.25 UNIT 3 INTRODUCTION TO WIRELESS AND MOBILE …
- 0.26 Introduction to Wireless Communications and Networks
- 0.27 Mobile communications: Basic concepts
- 0.28 Mobile Wireless Communications
- 0.29 wireless communications
- 1 📘 Introduction to Wireless and Mobile Communication
- 2 ✅ Basic Concepts
- 3 📶 Types of Wireless Communication
- 4 🧠 Applications
- 5 📚 Summary:
Wireless and Mobile Communication – Introduction & Basic Concepts
Wireless and mobile communication is the backbone of modern communication systems, enabling seamless connectivity across the world. It plays a crucial role in applications such as mobile phones, Wi-Fi, satellite communication, IoT, and 5G networks.
1. What is Wireless Communication?
Wireless communication is the transmission of information over a distance without using physical wires or cables. Instead, signals travel through air using electromagnetic waves like radio waves, microwaves, and infrared waves.
Key Characteristics of Wireless Communication
No physical medium (uses air or space)
Supports mobility (devices can move freely)
Uses radio frequencies for data transmission
Used in mobile networks, Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, satellites, etc.
2. What is Mobile Communication?
Mobile communication is a form of wireless communication where devices are portable and can move freely while remaining connected to a network. Examples include cellular networks (2G, 3G, 4G, 5G), Wi-Fi, and satellite communication.
Key Features of Mobile Communication
Supports mobility (users can move while communicating)
Uses cellular networks (divided into cells with towers)
Allows real-time voice and data transfer (calls, internet)
Provides global connectivity (via satellites and roaming)
3. Basic Components of Wireless & Mobile Communication
1. Transmitter – Converts information into signals (Example: Mobile phone, Wi-Fi router)
2. Receiver – Receives and decodes signals (Example: Another mobile phone, computer)
3. Medium (Channel) – Air or space where signals travel (Example: Radio waves, Infrared)
4. Antennas – Used to send and receive signals (Example: Mobile towers, satellite dishes)
5. Base Station (Cell Tower) – Connects mobile devices to the network
4. Types of Wireless Communication Technologies
A. Cellular Communication (Mobile Networks)
2G – Basic voice calls & SMS
3G – Faster internet (video calls, browsing)
4G LTE – High-speed internet, HD video streaming
5G – Ultra-fast speed, low latency, IoT, AI applications
B. Wireless LAN (Wi-Fi)
- Uses radio waves for high-speed local connectivity
- Example: Home Wi-Fi, public hotspots
C. Bluetooth
- Short-range wireless communication
- Used in headphones, smartwatches, file sharing
D. Satellite Communication
- Long-distance communication via satellites
- Used in TV broadcasting, GPS, military applications
E. Infrared (IR) Communication
- Used for short-range remote controls (TV remotes, sensors)
5. Advantages & Disadvantages of Wireless Communication
Advantages
No cables required (cost-effective)
Supports mobility (use devices anywhere)
Covers remote areas (via satellites)
Easy to expand networks
Disadvantages
Signal interference (from weather, obstacles)
Security risks (hacking, data theft)
Limited bandwidth (overcrowding of networks)
6. Applications of Wireless & Mobile Communication
Smartphones & Internet – Calls, browsing, messaging
GPS & Navigation – Google Maps, vehicle tracking
Healthcare – Telemedicine, remote patient monitoring
IoT (Internet of Things) – Smart homes, smart cities
Streaming & Media – YouTube, Netflix, live TV
Autonomous Vehicles – Self-driving cars, V2V communication
Conclusion
Wireless and mobile communication has transformed the world by enabling seamless, fast, and reliable connectivity. With advancements in 5G, AI, and IoT, future wireless networks will be smarter, faster, and more efficient.
Would you like a detailed explanation on any specific topic?
Wireless and Mobile Communication Introduction and Basic Concept
UNIT 1 INTRODUCTION TO MOBILE COMMUNICATIONS
UNIT 3 INTRODUCTION TO WIRELESS AND MOBILE …
Introduction to Wireless Communications and Networks
Mobile communications: Basic concepts
Mobile Wireless Communications
wireless communications
Here’s a clear and concise explanation of the Introduction and Basic Concepts of Wireless and Mobile Communication — useful for B.Tech, BCA, MCA, or competitive exams like GATE, UGC NET, and others.
📘 Introduction to Wireless and Mobile Communication
🔹 What is Wireless Communication?
Wireless communication is the transfer of information between two or more points without using wires or physical connections.
It uses radio waves, microwaves, infrared, or other electromagnetic signals.
🔹 What is Mobile Communication?
Mobile communication is a subset of wireless communication where the communicating devices can move freely while staying connected (like smartphones, laptops, tablets, etc.).
✅ Basic Concepts
1. Transmitter & Receiver
- Transmitter sends signals.
- Receiver receives them.
- Example: Your mobile phone transmits voice data to a tower.
2. Frequency Spectrum
- Wireless signals use part of the electromagnetic spectrum.
- Example bands: 900 MHz, 1800 MHz, 2.4 GHz (Wi-Fi)
3. Base Station
- A central point (like a mobile tower) that connects mobile devices to the network.
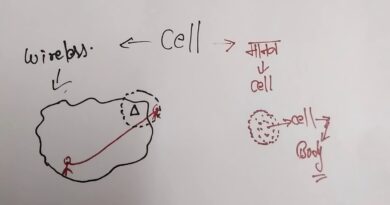
4. Cellular Concept
- The coverage area is divided into hexagonal cells.
- Each cell has a base station and operates on a specific frequency.
5. Handoff (Handover)
- When a mobile moves from one cell to another, the call or data session is transferred without interruption.
6. Duplexing
- Enables two-way communication.
- FDD (Frequency Division Duplexing): Different frequency for uplink/downlink.
- TDD (Time Division Duplexing): Same frequency, different time slots.
📶 Types of Wireless Communication
| Type | Example |
|---|---|
| Radio | FM, AM Radio |
| Microwave | Satellite, TV transmission |
| Infrared (IR) | Remote controls |
| Bluetooth | Wireless headphones |
| Wi-Fi | Home/Office networks |
| Cellular (GSM/4G/5G) | Mobile phones |
🧠 Applications
- Mobile phones
- Internet access
- GPS (Global Positioning System)
- Remote control systems
- IoT (Internet of Things)
📚 Summary:
| Term | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Wireless | No wires used to transmit data |
| Mobile | Wireless + Mobility |
| Frequency Spectrum | Bandwidth used for transmission |
| Cell | Area covered by one tower/base station |
| Handoff | Switching of cell during movement |
Would you like:
- A PDF notes on this topic?
- MCQs or GATE/UGC NET questions?
- A diagram-based explanation?
Let me know and I’ll provide what you need!