Replication techniques and its Types in Distributed Computing
Replication techniques and its Types in Distributed Computing.
Contents
Replication Techniques and Its Types in Distributed Computing
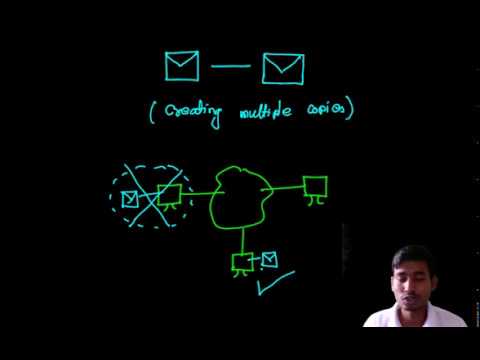
Replication in distributed computing refers to the process of creating and maintaining multiple copies of data or services across different nodes in a network. The primary goals of replication are fault tolerance, high availability, performance improvement, and load balancing.
1. Why is Replication Needed?
Fault Tolerance – Ensures system availability even if some nodes fail.
High Availability – Users can access data even if some replicas go down.
Load Balancing – Distributes requests across replicas to avoid bottlenecks.
Performance Improvement – Reduces latency by placing replicas closer to users.
Data Consistency – Ensures all nodes have the same updated data.
2. Types of Replication Techniques
A. Data Replication (Used in Databases & Storage Systems)
-
Synchronous Replication
- All copies are updated immediately before the transaction is committed.
- Ensures strong consistency but has high latency.
- Example: Banking transactions, financial systems.
-
Asynchronous Replication
- Changes are first made to one replica and then propagated to others later.
- Faster but may lead to temporary inconsistencies.
- Example: Cloud storage (Google Drive, Dropbox).
-
Semi-Synchronous Replication
- A middle ground where some replicas confirm updates before committing, but not all.
- Balances between consistency and speed.
B. Computation Replication (Used in Distributed Computing & Cloud Services)
-
Active Replication
- All replicas execute the same request in parallel.
- Ensures consistency but requires more resources.
- Used in fault-tolerant systems (e.g., flight control software).
-
Passive Replication (Primary-Backup Model)
- A primary node processes requests and updates secondary nodes.
- If the primary node fails, a backup takes over.
- Used in high-availability services like databases.
C. Hybrid Replication
- A combination of active and passive replication to balance performance and reliability.
- Example: Cloud-based distributed databases like Google Spanner.
3. Challenges in Replication
Consistency Issues – Ensuring all copies have the same data.
Network Latency – Syncing replicas across long distances takes time.
Conflict Resolution – Handling simultaneous updates from different nodes.
Storage Overhead – Keeping multiple copies requires extra space.
Would you like a more detailed explanation of any specific replication type?
Here’s a complete and easy-to-understand explanation of Replication Techniques and their Types in Distributed Computing, ideal for students preparing for exams like GATE, or anyone learning distributed systems.
🔁 What is Replication in Distributed Computing?
Replication refers to the process of maintaining multiple copies (replicas) of data or services across different nodes in a distributed system to ensure:
-
✅ High Availability
-
✅ Fault Tolerance
-
✅ Load Balancing
-
✅ Improved Performance
🔍 Why Replication is Important?
-
If one server fails, another replica can serve the request (fault tolerance).
-
It reduces latency by serving users from the nearest replica.
-
Enhances system reliability and scalability.
🧩 Types of Replication Techniques
1. Data Replication
Maintaining copies of data (files, database records) across multiple machines.
Types:
-
Full Replication: Entire dataset is replicated to all nodes
👉 High availability, but high storage cost. -
Partial Replication: Only selected data is replicated
👉 More efficient, but less redundant.
2. Synchronous vs Asynchronous Replication
🟩 Synchronous Replication
-
All replicas must be updated before the operation is considered complete.
-
Ensures strong consistency.
-
Slower due to network delays.
✅ Used in financial systems, where accuracy is critical.
🟨 Asynchronous Replication
-
Updates are sent to replicas after the operation completes at the primary.
-
Faster, but may cause temporary inconsistencies.
✅ Suitable for content delivery networks (CDNs) or backups.
3. Primary-Backup (Master-Slave) Replication
-
One node is the primary/master, others are backups/slaves.
-
All writes go to the master, which then replicates to the slaves.
-
Simple, but single point of failure unless failover is implemented.
4. Multi-Master Replication
-
Multiple nodes can accept read/write operations.
-
Conflict resolution mechanisms are needed.
-
More complex, but highly available and scalable.
✅ Used in collaborative apps, CRDTs, or eventually consistent databases.
5. State Machine Replication (SMR)
-
A system runs a replicated state machine across multiple nodes.
-
All replicas process the same sequence of inputs.
-
Requires consensus algorithms like Paxos or Raft.
✅ Used in distributed databases, blockchains, and fault-tolerant systems.
6. Quorum-Based Replication
-
A write or read must be acknowledged by a majority (quorum) of replicas.
-
Ensures consistency without needing to contact all replicas.
-
Balances performance and reliability.
✅ Used in Amazon DynamoDB, Cassandra, etc.
🧠 Summary Table
| Replication Type | Description | Best Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Full Replication | All data on all nodes | High availability, low-latency reads |
| Partial Replication | Only part of data is replicated | Saves space, custom distribution |
| Synchronous | Updates all replicas before completion | Strong consistency needed |
| Asynchronous | Updates replicas after completion | Performance-sensitive systems |
| Primary-Backup | One master handles writes | Simple fault-tolerant setup |
| Multi-Master | All nodes accept writes | High scalability |
| State Machine Replication | Identical replicas process same input log | High-reliability systems |
| Quorum-Based | Majority agreement ensures consistency | Scalable and resilient databases |
📘 Bonus: Real-World Examples
| System | Replication Used |
|---|---|
| Google Spanner | Synchronous + SMR (Paxos) |
| MongoDB | Primary-Backup (Replica Sets) |
| Cassandra | Quorum-Based + Eventually Consistent |
| Git | Full replication (DVCS) |
Would you like:
-
A visual diagram or chart of these types?
-
A comparison with consistency models?
-
A short quiz to test understanding?
Let me know!