Goals of Distributed System distribution network
Goals of Distributed System distribution network
Contents [hide]
- 1 Goals of a Distributed System in a Distribution Network
- 2 Transparency
- 3 Scalability
- 4 Fault Tolerance & Reliability
- 5 Resource Sharing
- 6 Performance
- 7 Security
- 8 Openness & Interoperability
- 9 Cost Efficiency
- 10 Conclusion
- 11 Distributed Systems LECTURE NOTES B.TECH IV YEAR
- 12 Distributed Systems [R17A0522] LECTURE NOTES
- 13 Goals of Distributed System distribution network
- 14 Distributed Systems Principles and Paradigms
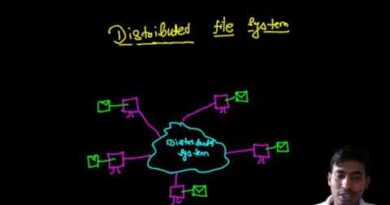
Goals of a Distributed System in a Distribution Network
A Distributed System is a collection of independent computers that appear to users as a single coherent system. In the context of a distribution network, it ensures efficient resource management, communication, and fault tolerance. The key goals of a distributed system in such a setup are:
Transparency
A distributed system should appear as a single system to users despite its underlying complexity. There are different types of transparency:
- Access Transparency → Users don’t need to know the location of resources.
- Location Transparency → Resources can be accessed without knowing their physical location.
- Replication Transparency → Multiple copies of data exist, but users see a single logical copy.
- Concurrency Transparency → Multiple users can access shared resources without conflicts.
- Failure Transparency → The system should continue operating despite failures.
Scalability
A distribution network should scale efficiently as the number of nodes, users, and data grows. It includes:
- Geographic Scalability → Supporting large distances (e.g., cloud data centers).
- Size Scalability → Handling a growing number of devices without performance degradation.
- Administrative Scalability → Supporting multiple organizations managing the network.
Fault Tolerance & Reliability
A distributed system should continue to operate even if some components fail:
- Redundancy → Backup components ensure continuous operation.
- Replication → Data is stored in multiple locations to avoid loss.
- Self-Healing → The system detects and recovers from failures automatically.
Resource Sharing
Efficient sharing of computing power, data, and network resources:
- Load Balancing → Distributing the workload evenly across multiple nodes.
- Distributed Databases → Ensuring data consistency and availability.
- Shared Computational Resources → Using cluster computing for heavy tasks.
Performance
The system should provide high speed and low latency for all users:
- Low Latency Communication → Optimized data transfer across nodes.
- Efficient Algorithms → Quick decision-making and processing.
- Caching & Replication → Storing frequently accessed data close to users.
Security
A distributed system must be secure against attacks, failures, and unauthorized access:
- Authentication & Authorization → Ensuring only authorized users access resources.
- Data Encryption → Protecting sensitive information during transmission.
- Failure & Attack Detection → Monitoring and responding to security threats.
Openness & Interoperability
The system should support different platforms, protocols, and technologies:
- Cross-Platform Support → Windows, Linux, macOS, etc.
- Open Standards → Support for common APIs and communication protocols.
- Extensibility → Easy integration with new services and technologies.
Cost Efficiency
A distributed system should minimize operational costs while maximizing performance:
- Efficient Resource Utilization → Using computing resources only when needed.
- Cloud Integration → Leveraging cloud computing for scalability and cost-effectiveness.
- Energy Efficiency → Reducing power consumption in large-scale networks.
Conclusion
The goals of a distributed system in a distribution network focus on transparency, scalability, fault tolerance, performance, security, interoperability, and cost efficiency. By achieving these objectives, a distributed system ensures seamless operations, high availability, and optimal resource usage.