LOGICAL CLOCK IN DISTRIBUTED SYSTEM HAPPENED BEFORE CLOCK CLOCK SYNC CLOCK VECTOR
LOGICAL CLOCK IN DISTRIBUTED SYSTEM HAPPENED BEFORE CLOCK CLOCK SYNC CLOCK VECTOR.
Distributed Systems Physical Clocks Logical Clocks Vector Clocks Synchronize Physical Clocks Logical Time Happened Before Clocks Linear Time Distributed Systems Physical Clocks Logical Clocks Vector Clocks.
Synchronize Physical Clocks Logical Time Happened Before Linear Time Time Ordering Module Vector Clock Vs Lamport Clock Logical Clock In Distributed System What Is Global Clock In Distributed System. Vector Clock In Distributed System Types Of Clocks In Distributed System Physical Clocks Logical Clocks Vector Clocks Synchronize Physical Clocks Logical Time Happened Before Linear Time Time Ordering Module Vector Clock Vs Lamport Clock. Logical Clock in Distributed System. What Is Global Clock In Distributed System Vector Clock In Distributed System Types Of Clocks In Distributed System Time Ordering Module. Vector Clock Vs Lamport Clock Logical Clock In Distributed System What Is Global Clock In Distributed System Vector Clock In Distributed System Types Of Clocks In Distributed System.
Here’s a clear and concise explanation of Logical Clocks in Distributed Systems, including concepts like Happened-Before Relation, Lamport Clock, Vector Clock, and Clock Synchronization.
Contents
- 1 🕒 LOGICAL CLOCK IN DISTRIBUTED SYSTEMS
- 1.1 🔄 1. Happened-Before Relation (→) – by Leslie Lamport
- 1.2 ⏱️ 2. Lamport’s Logical Clock (Scalar Clock)
- 1.3 🧭 3. Vector Clocks
- 1.4 🕰️ 4. Clock Synchronization
- 1.5 📊 Summary Table
- 1.6 ✅ Real-World Use
- 1.7 LOGICAL CLOCK IN DISTRIBUTED SYSTEM HAPPENED BEFORE CLOCK CLOCK SYNC CLOCK VECTOR
- 1.8 Clocks in Distributed System
🕒 LOGICAL CLOCK IN DISTRIBUTED SYSTEMS
In distributed systems, there’s no global clock. So, we use logical clocks to order events correctly across multiple processes (nodes).
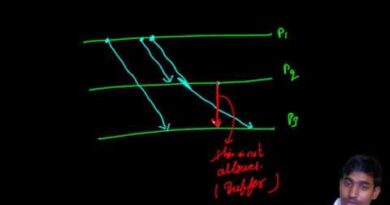
🔄 1. Happened-Before Relation (→) – by Leslie Lamport
This defines a partial order of events.
📌 Definition:
-
If A and B are events in the same process and A occurs before B →
A → B -
If A is sending a message and B is receiving the same →
A → B -
If
A → BandB → C→ thenA → C(transitivity)
Purpose: Establish a cause-effect relationship between events in different processes.
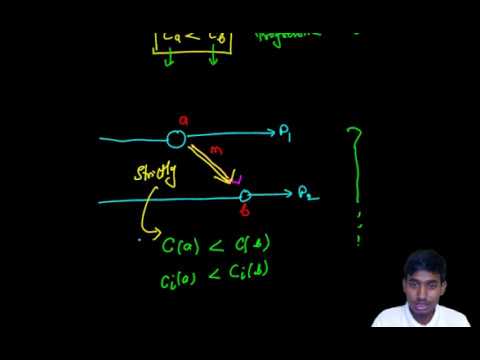
⏱️ 2. Lamport’s Logical Clock (Scalar Clock)
Goal: Assign numbers (timestamps) to events to maintain A → B ⇒ timestamp(A) < timestamp(B)
📌 Rules:
-
Each process maintains a local clock (initially 0).
-
Before executing any event, increment the clock:
C := C + 1 -
When sending a message, send timestamp with it.
-
On receiving a message with timestamp
T, set:C := max(C, T) + 1
Limitation:
-
It can say one event happened before another but not if two events are concurrent.
🧭 3. Vector Clocks
Goal: Detect causal relationships and concurrent events accurately.
📌 How it works:
-
Each process keeps a vector
V[i]of sizen(number of processes). -
Before event:
V[i] := V[i] + 1 -
On sending message, send vector.
-
On receiving message with vector
V':-
V[i] := V[i] + 1 -
For all
j ≠ i,V[j] := max(V[j], V'[j])
-
🔍 Comparison:
-
Event A happened before B ⇨
V(A) < V(B)(element-wise) -
Events concurrent ⇨
V(A)andV(B)are not comparable
🕰️ 4. Clock Synchronization
Since there’s no common clock:
-
NTP (Network Time Protocol): Sync real clocks (physical)
-
Cristian’s Algorithm: Get time from time server (1 request)
-
Berkeley Algorithm: Average times across nodes
These aim to reduce clock drift and keep system-wide time in sync, though not perfect.
📊 Summary Table
| Concept | Purpose | Can Detect Concurrency? | Type |
|---|---|---|---|
| Happened-Before | Partial ordering of events | Yes | Theory |
| Lamport Clock | Order events logically | No | Scalar |
| Vector Clock | Track causality + concurrency | Yes | Vector |
| Clock Sync (NTP) | Sync real-time clocks | Not logical ordering | Physical |
✅ Real-World Use
-
Databases (like Cassandra, DynamoDB) → use vector clocks for conflict resolution.
-
Distributed logs (Kafka) → maintain event order.
-
Debugging distributed systems → to trace event flows.
Would you like:
-
A diagram of these clocks in action?
-
Sample code in Python or Java to simulate this?
-
Or a PDF summary sheet for revision?
Let me know!