Multicast Ordering FIFO Ordering algorithm in distributed systems-Maker Activemq Client
Multicast Ordering FIFO Ordering algorithm in distributed systems-Maker Activemq Client
Contents
- 0.0.1 Multicast Ordering and FIFO Ordering in Distributed Systems – ActiveMQ Client Implementation
- 0.0.2 What is Multicast Ordering?
- 0.0.3 Definition
- 0.0.4 Types of Multicast Ordering
- 0.0.5 What is FIFO Ordering?
- 0.0.6 Definition
- 0.0.7 FIFO Ordering in ActiveMQ
- 0.0.8 Multicast Ordering in ActiveMQ (Publish/Subscribe)
- 0.0.9 Key Takeaways
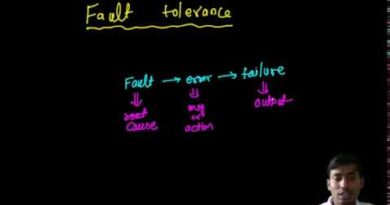
- 1 📡 Multicast & FIFO Ordering in Distributed Systems
Multicast Ordering and FIFO Ordering in Distributed Systems – ActiveMQ Client Implementation
In distributed systems, message ordering is crucial for maintaining consistency across different nodes. Two common ordering guarantees in message passing systems are Multicast Ordering and FIFO Ordering. These concepts are widely used in message brokers like ActiveMQ, which supports reliable message delivery across distributed components.
What is Multicast Ordering?
Definition
Multicast ordering ensures that all nodes in a distributed system receive messages in the same order when sent to a group. This is essential for applications requiring synchronized message delivery across multiple subscribers.
Types of Multicast Ordering
Causal Ordering – Ensures messages are received in the order they were causally related.
Total Ordering – Guarantees that all messages are received in the same order across all nodes.
FIFO Ordering – Ensures that messages from the same sender arrive in the order they were sent.
What is FIFO Ordering?
Definition
FIFO (First In, First Out) Ordering ensures that messages sent by a single sender are received in the same order by all receivers.
Example: If Node A sends messages M1 → M2 → M3, all receivers must receive them in the same order (M1 → M2 → M3).
Challenge: If messages take different network paths, network delays can disrupt FIFO ordering. Middleware like ActiveMQ ensures this ordering using message queues.
ActiveMQ Implementation for FIFO and Multicast OrderingApache ActiveMQ is a message broker that supports FIFO ordering and multicast messaging using topics and queues.
FIFO Ordering in ActiveMQ
- FIFO is guaranteed in Queues (point-to-point communication).
- Each message sent by a producer is delivered exactly once to a consumer in order.
Example: Java Implementation (ActiveMQ FIFO Queue)
FIFO Consumer
Ensures FIFO message delivery to consumers.
Multicast Ordering in ActiveMQ (Publish/Subscribe)
- Uses Topics instead of Queues.
- Messages are delivered in the same order to all subscribers.
Example: Java Implementation (Multicast Topic in ActiveMQ)
Multicast Subscriber
Ensures all subscribers receive messages in the same order.
Key Takeaways
FIFO Ordering ensures that messages from a single sender are received in order.
Multicast Ordering guarantees that all receivers get messages in the same order in a publish-subscribe system.
ActiveMQ provides built-in support for FIFO ordering (Queues) and Multicast ordering (Topics).
ActiveMQ makes distributed messaging efficient and reliable, ensuring order preservation in real-time applications like finance, IoT, and cloud systems.
Here’s a detailed explanation of Multicast Ordering and FIFO Ordering algorithms in Distributed Systems, especially in the context of ActiveMQ (or any message-oriented middleware) using a Maker-Consumer (Client) model.
📡 Multicast & FIFO Ordering in Distributed Systems
📘 With Maker-Consumer Model (ActiveMQ Client Example)
🔄 1. Multicast Communication in Distributed Systems
Multicast refers to sending a message from one sender to multiple receivers (clients/consumers) at the same time.
✅ Use Case:
-
Collaborative applications
-
Stock ticker updates
-
Chat systems
-
Distributed games
⏳ 2. Message Ordering in Multicast
In multicast, it’s important to maintain the correct order of messages so that all clients interpret the system state correctly.
Here are the common ordering strategies:
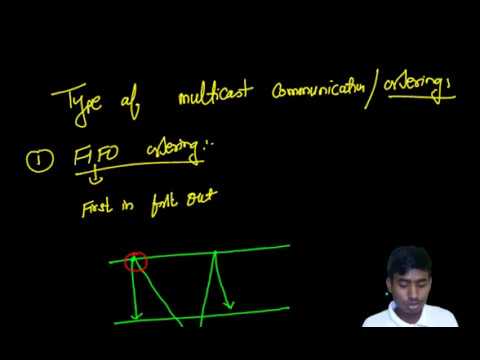
📌 a. FIFO Ordering (First-In-First-Out)
Definition:
Messages from the same sender are received by all recipients in the order they were sent.
Example:
If a sender sends messages M1, M2, M3, all receivers must see:
But FIFO does not guarantee global order across multiple senders.
📌 b. Causal Ordering
Definition:
Preserves the cause-effect relationship between messages.
-
If message M1 causes message M2, then all receivers must receive M1 before M2.
Technique:
-
Implemented using Vector Clocks.
📌 c. Total Ordering
Definition:
All messages (from all senders) are received in exactly the same order by all recipients.
Technique:
-
Use a central sequencer or a distributed consensus protocol (like Paxos or Raft).
🧪 Example with ActiveMQ (Maker-Consumer Model)
🧱 Architecture:
-
Maker (Producer) sends messages to a Topic (for multicast).
-
Consumers subscribe to the topic to receive updates.
💡 Implementing FIFO Ordering in ActiveMQ:
By default, ActiveMQ supports FIFO ordering per producer in a topic-based system.
✅ Steps:
-
Configure topic and durable consumers.
-
Use a single connection/session per producer to preserve order.
-
Set
MessageGroupIDto group messages logically (optional). -
Consumers process messages in the order they arrive from the broker.
🔧 Code Example (Java):
🛠️ Enhancing Ordering Across Multiple Producers
For global ordering, you must:
-
Use a central sequence manager
-
Or enforce synchronization at the application level
-
Or switch to partitioned topics with ordering per partition
🚧 Challenges in Distributed Ordering
-
Network latency
-
Message delays or loss
-
Clock synchronization (NTP or Lamport/Vector clocks)
-
Broker partitioning (if using clustered ActiveMQ)
✅ Summary Table
| Ordering Type | Guarantees | Use Case | Tools |
|---|---|---|---|
| FIFO | Order per sender | Simple logs, Chat | ActiveMQ w/ MessageGroupID |
| Causal | Cause-before-effect | Collaborative editing | Vector Clocks |
| Total | Global consistent order | Banking, Ledgers | Sequencer, Kafka w/ key |
Would you like:
-
A PowerPoint version for a presentation?
-
A PDF for study notes?
-
Code in Python or JavaScript with ActiveMQ client?
Let me know your preference!