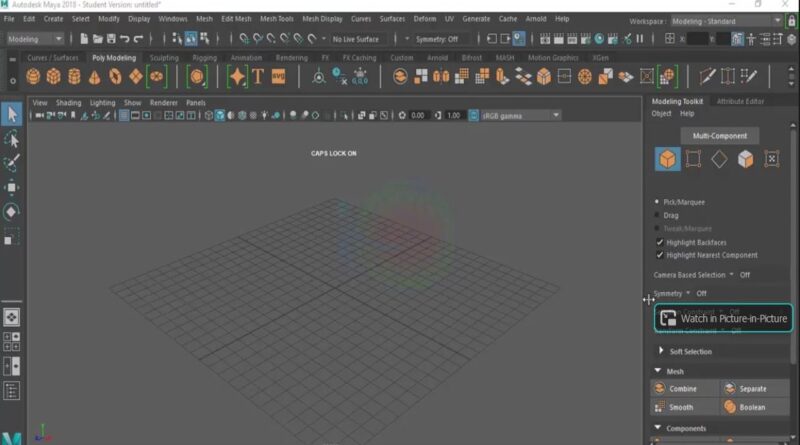
Modeling Sculpting Rigging Rendering FX-FX Catching Motion Graphics-Curves-Surfaces UV Arnold
Best software for creating 3D Animation and Modeling-Sculpting-Rigging-Rendering-FX-FX Catching-Motion Graphics-Curves-Surfaces-UV-Arnold.
It looks like you’re referring to various aspects of 3D modeling, animation, and rendering used in industries like VFX, gaming, and animation. Here’s a breakdown of these concepts:
Contents
- 0.1 1. Modeling & Sculpting
- 0.2 2. Rigging
- 0.3 3. Rendering & FX
- 0.4 4. Motion Graphics & Animation
- 0.5 5. UV Mapping & Texturing
- 0.6 Modeling Sculpting Rigging Rendering FX-FX Catching Motion Graphics-Curves-Surfaces UV Arnold
- 0.7 B.SC A&GD (Animation and Graphics Designing)
- 1 🎨 1. Modeling
- 2 🗿 2. Sculpting
- 3 🧍♂️ 3. Rigging
- 4 🎥 4. Rendering
- 5 💥 5. FX / FX Catching
- 6 🎞️ 6. Motion Graphics
- 7 🌀 7. Curves and Surfaces
- 8 📐 8. UV Mapping
- 9 🧩 How They Work Together (Pipeline Summary)
- 10 🎯 Want to Learn?
1. Modeling & Sculpting
- Modeling: Creating 3D objects using polygons, vertices, and edges (e.g., Maya, Blender, 3ds Max).
- Sculpting: High-detail modeling for organic shapes (e.g., ZBrush, Mudbox).
2. Rigging
- Creating a skeleton (bones & joints) for 3D models so they can move.
- Used in character animation and mechanical simulations.
3. Rendering & FX
- Rendering: Converting a 3D model into a 2D image (e.g., Arnold, V-Ray, Redshift).
- FX & FX Caching: Simulating physics-based effects like fire, smoke, and water (e.g., Houdini, RealFlow).
4. Motion Graphics & Animation
- Curves & Surfaces: Creating smooth animations and transitions in 3D design.
- Motion Graphics: Used for text animations, UI design, and visual effects (e.g., After Effects, Cinema 4D).
5. UV Mapping & Texturing
- UV Unwrapping: Flattening a 3D object into a 2D space for texturing.
- Used in game development, movies, and CGI.
Would you like more details on a specific area like texturing, rigging, or rendering?
Modeling Sculpting Rigging Rendering FX-FX Catching Motion Graphics-Curves-Surfaces UV Arnold
B.SC A&GD (Animation and Graphics Designing)
You’re touching on a wide range of 3D production pipeline elements—each a crucial part of creating high-end animation, visual effects, and motion graphics. Here’s a clear breakdown of these terms and how they fit together in real-world workflows (like in Maya, Blender, Houdini, Cinema 4D, etc.):
🎨 1. Modeling
-
What: Creating the 3D shape or structure of characters, props, or environments.
-
Tools: Polygons, NURBS, subdivision surfaces.
-
Software: Blender, Autodesk Maya, ZBrush, 3ds Max.
Example: Sculpting a human face or building a sci-fi spaceship model.
🗿 2. Sculpting
-
What: High-resolution detail creation using brush-based tools (like clay).
-
Purpose: Add realistic wrinkles, muscles, and textures.
-
Software: ZBrush, Mudbox, Blender’s Sculpt Mode.
Often used to generate normal maps or displacement maps for real-time rendering.
🧍♂️ 3. Rigging
-
What: Building a skeleton or control system so characters or objects can move.
-
Includes:
-
Joints/Bones
-
IK (Inverse Kinematics)
-
FK (Forward Kinematics)
-
Blend shapes (for facial expressions)
-
Software: Maya, Blender, Houdini.
🎥 4. Rendering
-
What: Turning the 3D scene into a 2D image or animation.
-
Includes: Lighting, shadows, reflections, ambient occlusion.
-
Render Engines:
-
Arnold (high-quality, used in Maya)
-
Cycles/Eevee (Blender)
-
V-Ray, Redshift
-
Arnold is widely used in film-quality projects for physically accurate lighting.
💥 5. FX / FX Catching
-
FX (Effects): Simulation of natural phenomena like smoke, fire, explosions, cloth, water.
-
FX Catching: Refers to how simulations interact with or affect geometry (like catching fire on a surface).
-
Software: Houdini (industry leader), Maya Bifrost, Blender Mantaflow.
🎞️ 6. Motion Graphics
-
What: Animated design elements, often 2D/3D text, shapes, icons used in intros, ads, videos.
-
Used In: Title sequences, UI animations, VFX transitions.
-
Software: After Effects, Cinema 4D (often with Redshift), Blender.
🌀 7. Curves and Surfaces
-
Curves: Paths that define shapes or motion (e.g., animation splines, NURBS curves).
-
Surfaces: Generated from curves (like extrusions, revolutions).
-
Used for organic and precise modeling (vehicles, architecture).
NURBS (Non-Uniform Rational B-Splines) are crucial in automotive and industrial design.
📐 8. UV Mapping
-
What: Unwrapping 3D models to lay them out in 2D space for texturing.
-
Tools: UV Editor, seams, unwrapping, pinning.
-
Goal: Make textures apply correctly without distortion.
Arnold and other renderers rely on accurate UVs for procedural and image-based texturing.
🧩 How They Work Together (Pipeline Summary)
🎯 Want to Learn?
Would you like:
-
A free beginner course roadmap?
-
Suggestions for YouTube channels or courses (Maya, Blender, Houdini)?
-
A visual diagram of the 3D pipeline?
Just tell me your preferred software or level (beginner/intermediate/pro) and I’ll tailor it for you!