System Programming: System Programming Tutorial-concept of assembly language-Assembler and it’s working with diagram
System Programming: System Programming Tutorial-concept of assembly language-Assembler and it’s working with diagram.
Contents
- 0.1 System Programming: Assembly Language and Assembler
- 0.2 1. Introduction to Assembly Language
- 0.3 Features of Assembly Language
- 0.4 2. What is an Assembler?
- 0.5 Assembler Functions:
- 0.6 3. Working of an Assembler (With Diagram)
- 0.7 Step-by-Step Assembler Workflow:
- 0.8 Diagram: Working of an Assembler
- 0.9 4. Types of Assemblers
- 0.10 1. Single-Pass Assembler
- 0.11 2. Two-Pass Assembler
- 0.12 5. Conclusion
- 0.13 System Programming: System Programming Tutorial-concept of assembly language-Assembler and it’s working with diagram
- 0.14 The Art of Assembly Language
- 0.15 Unit 1 What is System Programming?
- 1 📘 System Programming Tutorial – Assembly Language & Assembler
- 2 🧠 What is Assembly Language?
- 3 🛠️ What is an Assembler?
- 4 🔧 Working of Assembler – Step-by-Step
- 5 📊 Diagram – Working of an Assembler
- 6 📌 Symbol Table Example
- 7 📘 Example Code & Machine Code Translation
- 8 ✅ Summary
System Programming: Assembly Language and Assembler
1. Introduction to Assembly Language
Assembly Language is a low-level programming language that provides a direct mapping to a computer’s machine code. It is written using mnemonics instead of binary opcodes, making it easier for humans to read and write.
Features of Assembly Language
Uses symbolic mnemonics (e.g., MOV, ADD, SUB).
Provides direct hardware control.
Faster execution compared to high-level languages.
Requires an Assembler to convert it into machine code.
2. What is an Assembler?
An Assembler is a system program that translates assembly language into machine code (binary form) that a computer’s CPU can execute.
Assembler Functions:
- Converts mnemonics into opcodes (e.g.,
MOV A, B→78H). - Allocates memory for instructions and data.
- Handles labels and addresses (symbol table management).
- Detects syntax errors in the assembly code.
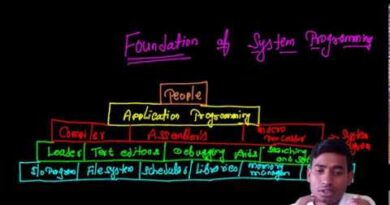
3. Working of an Assembler (With Diagram)
Step-by-Step Assembler Workflow:
-
Input: Assembly Program
- Programmer writes instructions using mnemonics.
- Example code:
-
Lexical Analysis
- The assembler scans the program and extracts mnemonics, labels, and operands.
-
Syntax Analysis
- Checks for errors like invalid mnemonics or incorrect operand usage.
-
Symbol Table Generation
- Creates a table of labels and their corresponding addresses.
-
Opcode Conversion
- Converts mnemonics into machine code instructions.
-
Address Resolution
- Assigns memory addresses to instructions and data.
-
Output: Machine Code (Object File)
- Generates an executable binary code.
Diagram: Working of an Assembler
4. Types of Assemblers
1. Single-Pass Assembler
- Processes code in one scan.
- Fast but struggles with forward references.
- Example: Basic 8-bit microcontrollers.
2. Two-Pass Assembler
- Pass 1: Creates a symbol table.
- Pass 2: Converts mnemonics to machine code using the symbol table.
- Example: Intel 8086 assembler.
5. Conclusion
- Assembly Language provides direct hardware control and efficient execution.
- Assemblers translate it into machine code using symbol tables, opcode conversion, and address resolution.
- Multi-pass assemblers handle forward references more efficiently.
Would you like a real-world example of an assembly program and its machine code conversion?
System Programming: System Programming Tutorial-concept of assembly language-Assembler and it’s working with diagram
The Art of Assembly Language
Unit 1 What is System Programming?
Here’s a comprehensive tutorial on System Programming, focusing on the Concept of Assembly Language, Assembler, and its working with a diagram.
📘 System Programming Tutorial – Assembly Language & Assembler
📌 What is System Programming?
System Programming involves creating system software like compilers, assemblers, linkers, loaders, operating systems, etc., that manage and control computer hardware.
🧠 What is Assembly Language?
Assembly Language is a low-level programming language that uses mnemonics (symbols or short codes) to represent machine-level instructions.
🔤 Example:
Each instruction corresponds to a machine instruction understood by the CPU.
🛠️ What is an Assembler?
An Assembler is a system program that converts assembly language code into machine code (binary).
🔄 Types of Assemblers:
-
Single-pass assembler: Processes code once. Faster, but limited functionality.
-
Two-pass assembler: Processes code twice. First pass builds the symbol table; second pass generates machine code.
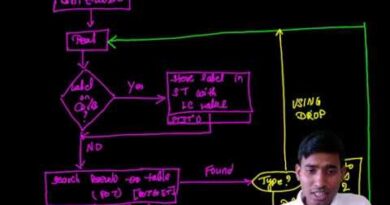
🔧 Working of Assembler – Step-by-Step
✨ Input:
-
Source code in assembly language (
.asmfile)
📥 Output:
-
Machine code or object code (
.objfile)
✅ Steps in Assembler Processing (Two-Pass Example)
Pass 1 – Analysis Phase:
-
Scans source code
-
Identifies labels, instructions, directives
-
Builds Symbol Table
-
Determines memory locations (addresses)
Pass 2 – Synthesis Phase:
-
Replaces mnemonics with machine code
-
Resolves label addresses using the Symbol Table
-
Produces final machine-level code
📊 Diagram – Working of an Assembler
📌 Symbol Table Example
| Label | Address |
|---|---|
| LOOP | 1003 |
| END | 1010 |
Assembler uses this during Pass 2 to fill in actual addresses for jumps or labels.
📘 Example Code & Machine Code Translation
Assembly Code:
Machine Code:
✅ Summary
| Concept | Description |
|---|---|
| Assembly Language | Low-level language using mnemonics |
| Assembler | Translates assembly code to machine code |
| Symbol Table | Keeps track of labels and addresses |
| Machine Code Output | Binary code that CPU executes |
Would you like a downloadable PDF with diagrams and exercises or a video-based explanation of this tutorial? I can also add practice problems with solutions for better understanding.